Word storms
Here is a visualisation of the accepted papers at ICML in the form of a word storm, which is a group of word clouds. The clouds are arranged so that if the same word appears in two clouds, it is in the same position. Hopefully this makes it easier to see the difference between clouds.
Word storms by Quim Castella Charles Sutton.
Session 1A — Optimization algorithms 1
chair Elad Hazan, room AT LT 4
-
On the Equivalence between Herding and Conditional Gradient Algorithms
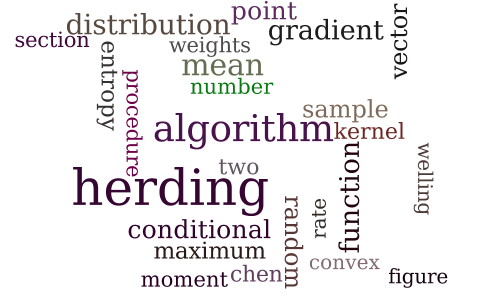
-
Similarity Learning for Provably Accurate Sparse Linear Classification

-
Stochastic Smoothing for Nonsmooth Minimizations: Accelerating SGD by Exploiting Structure

-
Making Gradient Descent Optimal for Strongly Convex Stochastic Optimization
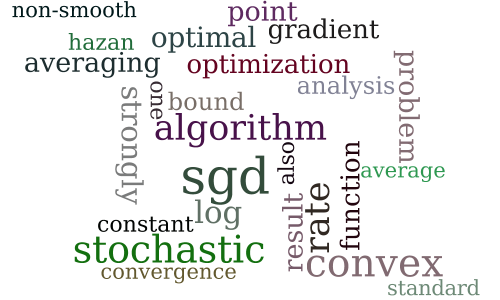
-
Scaling Up Coordinate Descent Algorithms for Large ℓ_1 Regularization Problems

-
Quasi-Newton Methods: A New Direction

-
A Hybrid Algorithm for Convex Semidefinite Optimization
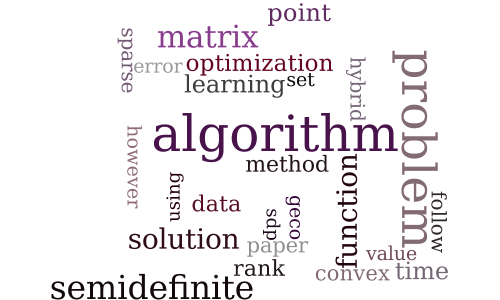
-
Efficient and Practical Stochastic Subgradient Descent for Nuclear Norm Regularization

Session 1B — Reinforcement learning 1
chair David Silver, room AT LT 5
-
Policy Gradients with Variance Related Risk Criteria
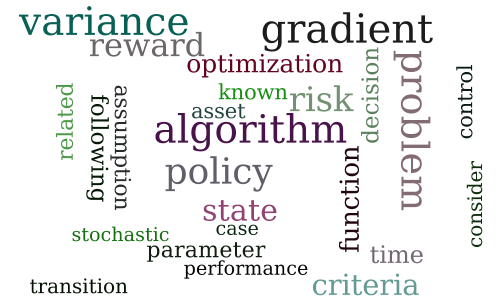
-
Approximate Dynamic Programming By Minimizing Distributionally Robust Bounds

-
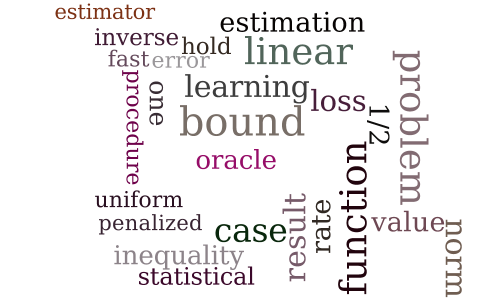
Statistical linear estimation with penalized estimators: an application to reinforcement learning
-
Approximate Modified Policy Iteration

-
A Dantzig Selector Approach to Temporal Difference Learning

-
Linear Off-Policy Actor-Critic

-
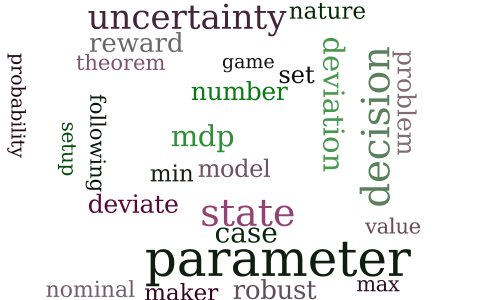
Lightning Does Not Strike Twice: Robust MDPs with Coupled Uncertainty
-
Bounded Planning in Passive POMDPs

Session 1C — Neural networks and deep learning 1
chair Marc'Aurelio Ranzato, room AT LT 1
-
Scene parsing with Multiscale Feature Learning, Purity Trees, and Optimal Covers

-
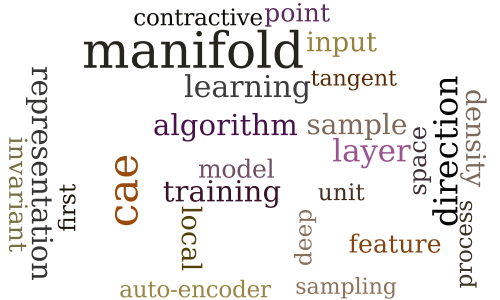
A Generative Process for Contractive Auto-Encoders
-
Deep Lambertian Networks

-
Deep Mixtures of Factor Analysers

-
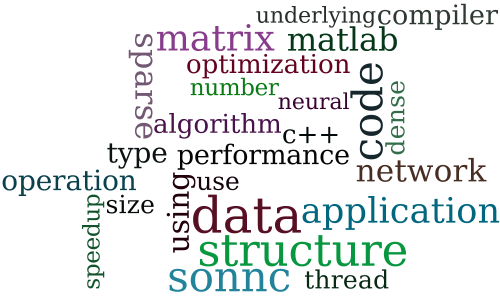
Utilizing Static Analysis and Code Generation to Accelerate Neural Networks
-
Estimating the Hessian by Back-propagating Curvature

-
Training Restricted Boltzmann Machines on Word Observations

-
A fast and simple algorithm for training neural probabilistic language models
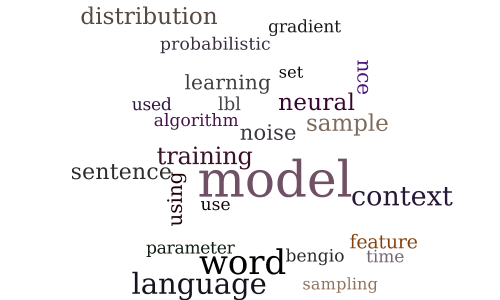
Session 1D — Structured output prediction
chair David McAllester, room AT LT 2
-
Learning to Identify Regular Expressions that Describe Email Campaigns

-
Efficient Structured Prediction with Latent Variables for General Graphical Models
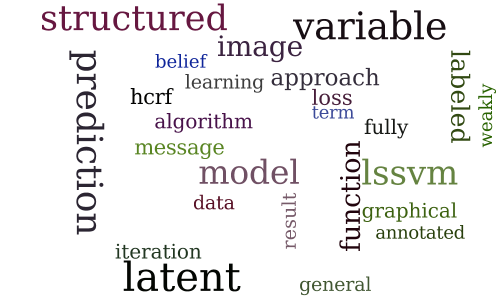
-
Output Space Search for Structured Prediction
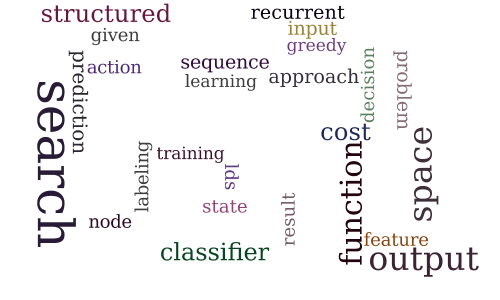
-
Efficient Decomposed Learning for Structured Prediction

-
Modeling Latent Variable Uncertainty for Loss-based Learning

Session 2A — Kernel methods 1
chair Arthur Gretton, room AT LT 4
-
On the Size of the Online Kernel Sparsification Dictionary

-
Improved Nystrom Low-rank Decomposition with Priors
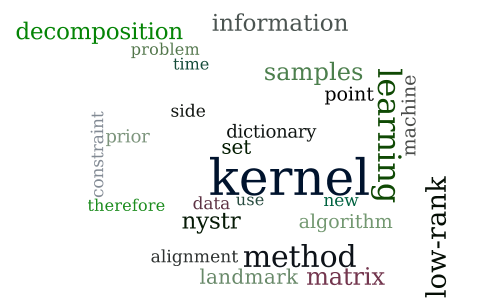
-
Bayesian Efficient Multiple Kernel Learning

-
A Binary Classification Framework for Two-Stage Multiple Kernel Learning

-
Multiple Kernel Learning from Noisy Labels by Stochastic Programming

-
Subgraph Matching Kernels for Attributed Graphs
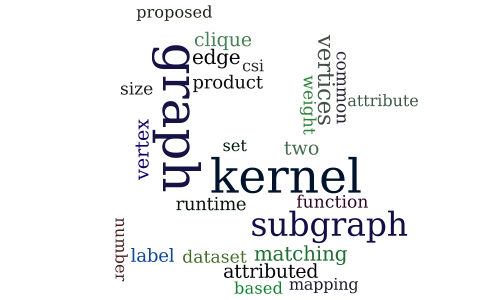
-
Fast Computation of Subpath Kernel for Trees
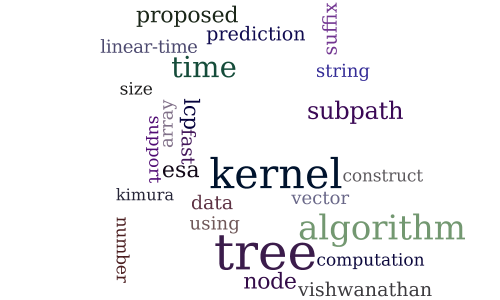
-
Hypothesis testing using pairwise distances and associated kernels

Session 2B — Reinforcement learning 2
chair Geoff Gordon, room AT LT 5
-
No-Regret Learning in Extensive-Form Games with Imperfect Recall

-
Near-Optimal BRL using Optimistic Local Transitions

-
Continuous Inverse Optimal Control with Locally Optimal Examples

-
Monte Carlo Bayesian Reinforcement Learning

-
Apprenticeship Learning for Model Parameters of Partially Observable Environments
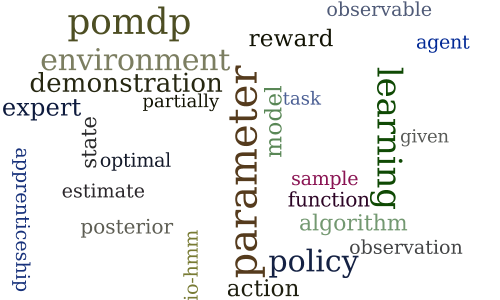
Session 2C — Gaussian processes
chair Ryan Adams, room AT LT 1
-
Gaussian Process Regression Networks

-
Infinite Tucker Decomposition: Nonparametric Bayesian Models for Multiway Data Analysis
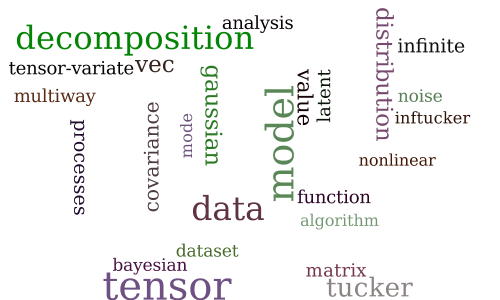
-
State-Space Inference for Non-Linear Latent Force Models with Application to Satellite Orbit Prediction
-
Gaussian Process Quantile Regression using Expectation Propagation

-
Residual Components Analysis

-
Manifold Relevance Determination

Session 2D — Statistical methods
chair Lawrence Carin, room AT LT 2
-
Lognormal and Gamma Mixed Negative Binomial Regression

-
Group Sparse Additive Models
-
Variance Function Estimation in High-dimensions
-
Sparse Additive Functional and Kernel CCA

-
Consistent Covariance Selection From Data With Missing Values

-
Conditional Sparse Coding and Grouped Multivariate Regression

-
Is margin preserved after random projection?
Session 3A — Optimization algorithms 2
chair Tong Zhang, room AT LT 4
-
A Discrete Optimization Approach for Supervised Ranking with an Application to Reverse-Engineering Quality Ratings

-
A Proximal-Gradient Homotopy Method for the L1-Regularized Least-Squares Problem

-
Complexity Analysis of the Lasso Regularization Path

-
Randomized Smoothing for (Parallel) Stochastic Optimization

Session 3B — Clustering 1
chair Shai Ben-David, room AT LT 5
-
Demand-Driven Clustering in Relational Domains for Predicting Adverse Drug Events

-
Clustering to Maximize the Ratio of Split to Diameter

-
An Iterative Locally Linear Embedding Algorithm

-
Robust Multiple Manifold Structure Learning

-
A Split-Merge Framework for Comparing Clusterings
-
On the Difficulty of Nearest Neighbor Search

Session 3C — Privacy, Anonymity, and Security
chair Tobias Scheffer, room AT LT 1
-
Bayesian Watermark Attacks

-
Poisoning Attacks against Support Vector Machines

-
Convergence Rates for Differentially Private Statistical Estimation

-
Finding Botnets Using Minimal Graph Clusterings
Session 3D — Ranking and Preference Learning
chair Balazs Kegl, room AT LT 2
-
Incorporating Domain Knowledge in Matching Problems via Harmonic Analysis

-
Consistent Multilabel Ranking through Univariate Losses

-
Predicting Consumer Behavior in Commerce Search
-
Adaptive Regularization for Similarity Measures

-
Online Structured Prediction via Coactive Learning

-
TrueLabel + Confusions: A Spectrum of Probabilistic Models in Analyzing Multiple Ratings
Session 3E — Nonparametric Bayesian inference
chair Sharon Goldwater, room AT LT 3
-
Factorized Asymptotic Bayesian Hidden Markov Models

-
An Infinite Latent Attribute Model for Network Data

-
The Nonparametric Metadata Dependent Relational Model
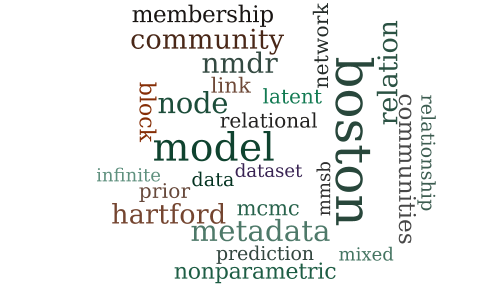
-
Dependent Hierarchical Normalized Random Measures for Dynamic Topic Modeling
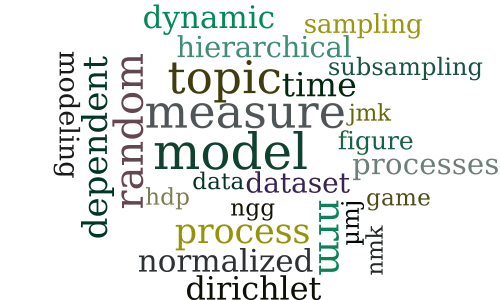
-
A Hierarchical Dirichlet Process Model with Multiple Levels of Clustering for Human EEG Seizure Modeling

-
Modeling Images using Transformed Indian Buffet Processes
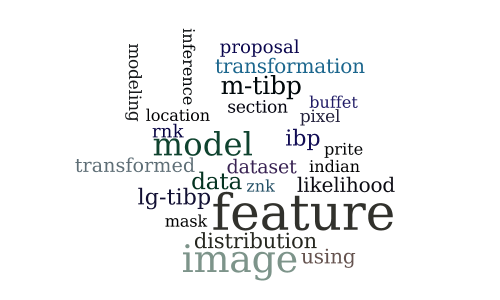
-
A Topic Model for Melodic Sequences
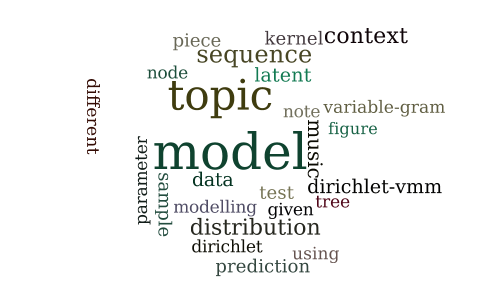
Session 4A — Feature selection and dimensionality reduction 1
chair Kilian Weinberger, room AT LT 4
-
Discovering Support and Affiliated Features from Very High Dimensions

-
Inferring Latent Structure From Mixed Real and Categorical Relational Data
-
Conditional Likelihood Maximization: A Unifying Framework for Information Theoretic Feature Selection
-
Dimensionality Reduction by Local Discriminative Gaussians

-
Fast Prediction of New Feature Utility

Session 4B — Online learning 1
chair Satyen Kale, room AT LT 5
-
An Online Boosting Algorithm with Theoretical Justifications

-
An adaptive algorithm for finite stochastic partial monitoring
-
Online Alternating Direction Method

-
Projection-free Online Learning

-
PAC Subset Selection in Stochastic Multi-armed Bandits

-
On Local Regret

-
Exact Soft Confidence-Weighted Learning

-
Compact Hyperplane Hashing with Bilinear Functions
Session 4C — Supervised learning 1
chair Cynthia Rudin, room AT LT 1
-
Improved Information Gain Estimates for Decision Tree Induction

-
Unachievable Region in Precision-Recall Space and Its Effect on Empirical Evaluation

-
The Big Data Bootstrap

-
Robust Classification with Adiabatic Quantum Optimization

-
Nonparametric Link Prediction in Dynamic Networks
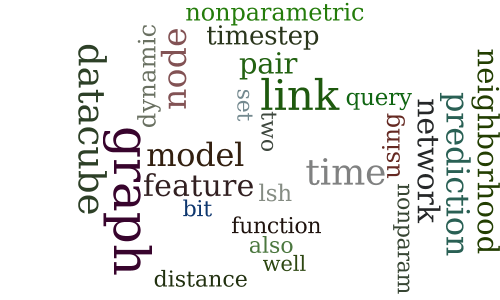
-
A Unified Robust Classification Model
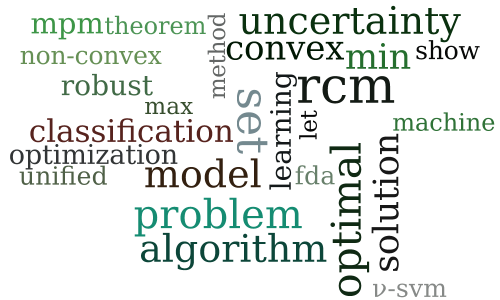
-
Maximum Margin Output Coding

-
Structured Learning from Partial Annotations

Session 4D — Transfer and Multi-Task Learning
chair Jenn Wortman Vaughan, room AT LT 2
-
Marginalized Denoising Autoencoders for Domain Adaptation

-
Information-Theoretical Learning of Discriminative Clusters for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation

-
Learning Task Grouping and Overlap in Multi-task Learning

-
A Convex Feature Learning Formulation for Latent Task Structure Discovery

-
Convex Multitask Learning with Flexible Task Clusters
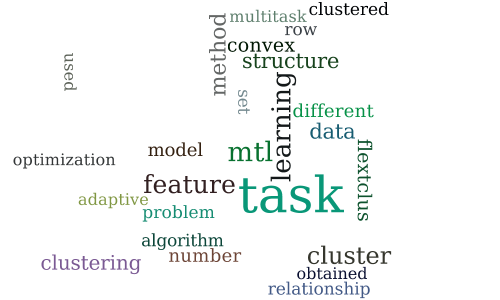
-
A Complete Analysis of the l_1,p Group-Lasso

-
Learning with Augmented Features for Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation

-
Cross-Domain Multitask Learning with Latent Probit Models

Session 4E — Graphical models
chair Matthias Seeger, room AT LT 3
-
High Dimensional Semiparametric Gaussian Copula Graphical Models
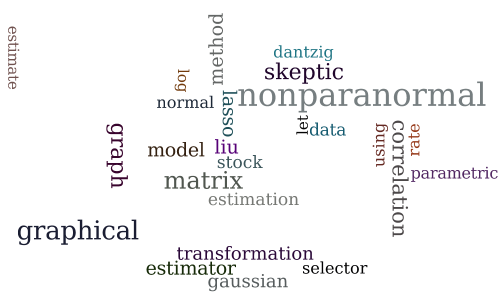
-
Convergence Rates of Biased Stochastic Optimization for Learning Sparse Ising Models

-
On the Partition Function and Random Maximum A-Posteriori Perturbations
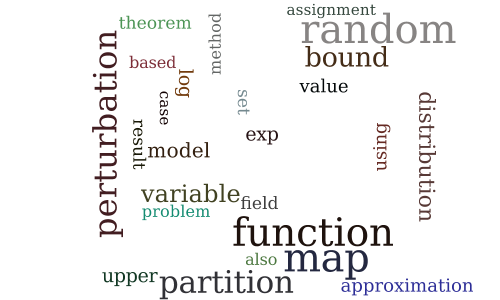
-
Anytime Marginal MAP Inference

-
Exact Maximum Margin Structure Learning of Bayesian Networks
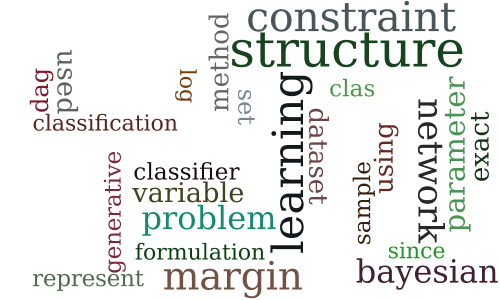
-
LPQP for MAP: Putting LP Solvers to Better Use

-
How To Grade a Test Without Knowing the Answers — A Bayesian Graphical Model for Adaptive Crowdsourcing and Aptitude Testing

-
Smoothness and Structure Learning by Proxy

Session 5A — Learning theory
chair Daniel Hsu, room AT LT 4
-
Linear Regression with Limited Observation

-
Optimizing F-measure: A Tale of Two Approaches

-
Conditional mean embeddings as regressors
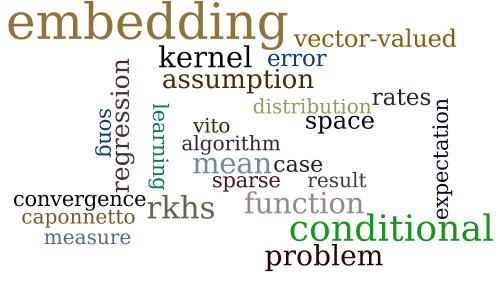
-
PAC-Bayesian Generalization Bound on Confusion Matrix for Multi-Class Classification

-
Tighter Variational Representations of f-Divergences via Restriction to Probability Measures

-
Agglomerative Bregman Clustering

-
The Convexity and Design of Composite Multiclass Losses
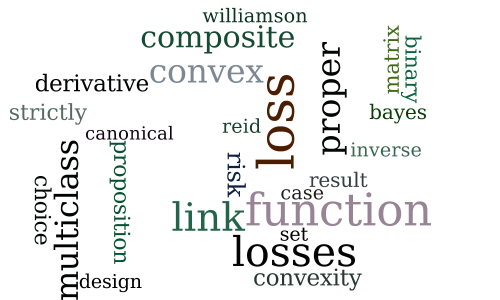
-
Minimizing The Misclassification Error Rate Using a Surrogate Convex Loss

Session 5B — Online learning 2
chair Csaba Szepesvari, room AT LT 5
-
Hierarchical Exploration for Accelerating Contextual Bandits

-
Online Bandit Learning against an Adaptive Adversary: from Regret to Policy Regret

-
Decoupling Exploration and Exploitation in Multi-Armed Bandits

-
Learning the Experts for Online Sequence Prediction

-
Plug-in martingales for testing exchangeability on-line
-
Parallelizing Exploration-Exploitation Tradeoffs with Gaussian Process Bandit Optimization

-
On-Line Portfolio Selection with Moving Average Reversion

-
Exponential Regret Bounds for Gaussian Process Bandits with Deterministic Observations

Session 5C — Neural networks and deep learning 2
chair Yoshua Bengio, room AT LT 1
-
Large-Scale Feature Learning With Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding

-
Learning Invariant Representations with Local Transformations

-
Building high-level features using large scale unsupervised learning

-
On multi-view feature learning

-
Learning to Label Aerial Images from Noisy Data

Session 5D — Sparsity and compressed sensing
chair Mahdi Milani Fard, room AT LT 2
-
Small-sample brain mapping: sparse recovery on spatially correlated designs with randomization and clustering

-
Estimation of Simultaneously Sparse and Low Rank Matrices

-
Multi-level Lasso for Sparse Multi-task Regression

-
Efficient Euclidean Projections onto the Intersection of Norm Balls

-
Learning Efficient Structured Sparse Models

Session 5E — Latent-Variable Models and Topic Models
chair Jordan Boyd-Graber, room AT LT 3
-
Max-Margin Nonparametric Latent Feature Models for Link Prediction
-
Canonical Trends: Detecting Trend Setters in Web Data
-
Variational Inference in Non-negative Factorial Hidden Markov Models for Efficient Audio Source Separatio
-
Sparse stochastic inference for latent Dirichlet allocation

-
Dirichlet Process with Mixed Random Measures: A Nonparametric Topic Model for Labeled Data

-
Rethinking Collapsed Variational Bayes Inference for LDA

-
Capturing topical content with frequency and exclusivity
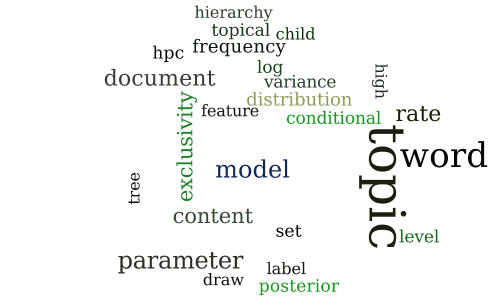
Session 6A — Semi-supervised learning
chair Maria Florina Balcan, room AT LT 4
-
A convex relaxation for weakly supervised classifiers

-
Semi-Supervised Learning of Class Balance under Class-Prior Change by Distribution Matching

-
A Simple Algorithm for Semi-supervised Learning with Improved Generalization Error Bound

-
Information-theoretic Semi-supervised Metric Learning via Entropy Regularization

-
Cross Language Text Classification via Subspace Co-regularized Multi-view Learning

-
Using CCA to improve CCA: A new spectral method for estimating vector models of words

-
Semi-Supervised Collective Classification via Hybrid Label Regularization
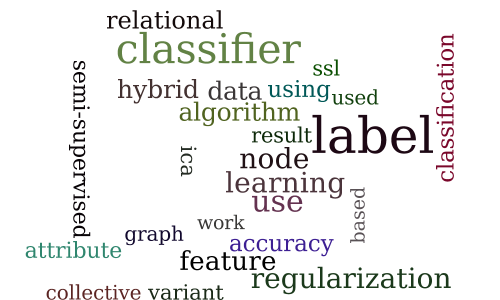
Session 6B — Reinforcement learning 3
chair Ron Parr, room AT LT 5
-
Compositional Planning Using Optimal Option Models
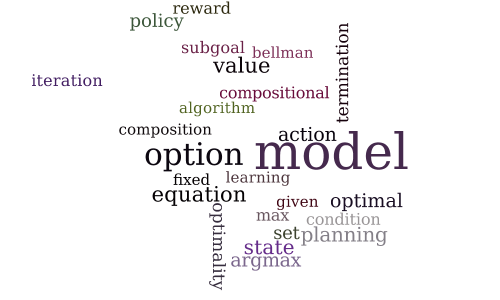
-
Learning Parameterized Skills

-
Safe Exploration in Markov Decision Processes
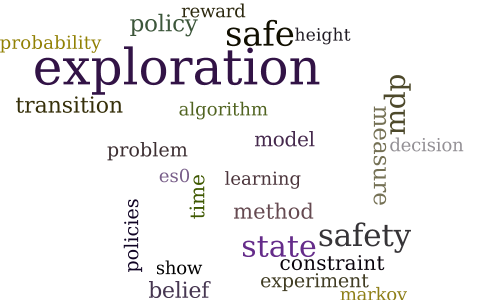
-
Modelling transition dynamics in MDPs with RKHS embeddings

Session 6C — Applications
chair Tom Dietterich, room AT LT 1
-
A Joint Model of Language and Perception for Grounded Attribute Learning

-
Predicting Manhole Events in New York City

-
Modeling Temporal Dependencies in High-Dimensional Sequences: Application to Polyphonic Music Generation and Transcription

-
Learning Object Arrangements in 3D Scenes using Human Context
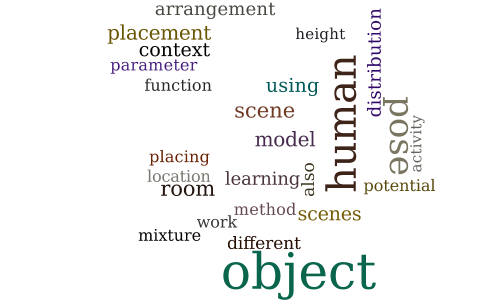
Session 6D — Time-Series Analysis
chair Naoki Abe, room AT LT 2
-
Learning the Dependence Graph of Time Series with Latent Factors
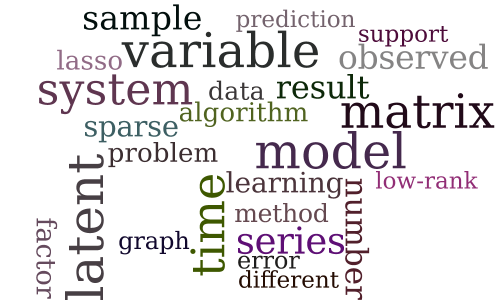
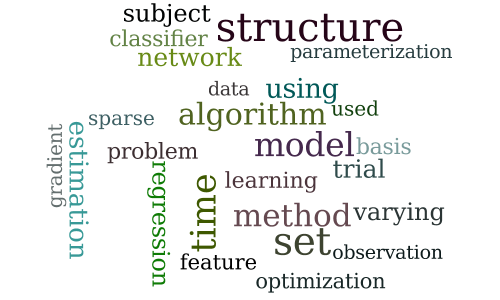
-
Improved Estimation in Time Varying Models
-
Bayesian Conditional Cointegration

-
Sparse-GEV: Sparse Latent Space Model for Multivariate Extreme Value Time Serie Modeling
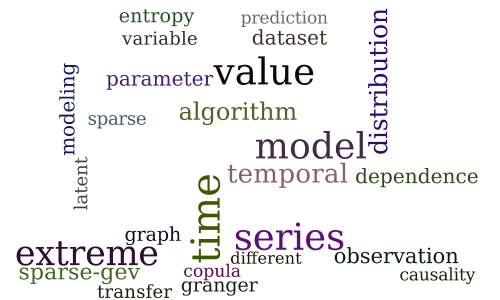
Session 6E — Graph-based learning
chair Charles Elkan, room AT LT 3
-
Shortest path distance in random k-nearest neighbor graphs

-
Submodular Inference of Diffusion Networks from Multiple Trees

-
Influence Maximization in Continuous Time Diffusion Networks
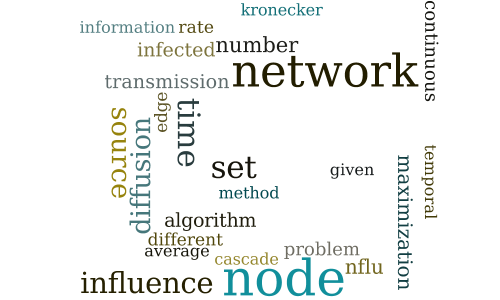
-
Latent Multi-group Membership Graph Model

-
The Most Persistent Soft-Clique in a Set of Sampled Graphs
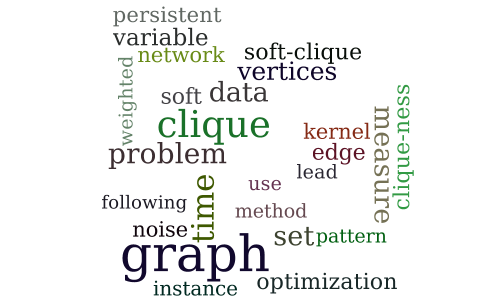
-
Two Manifold Problems with Applications to Nonlinear System Identification

-
Incorporating Causal Prior Knowledge as Path-Constraints in Bayesian Networks and Maximal Ancestral Graphs

Session 7A — Invited Applications
chair Samy Bengio, room AT LT 4
-
Conversational Speech Transcription Using Context-Dependent Deep Neural Networks
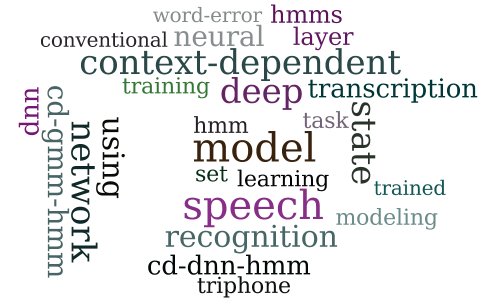
-
Data-driven Web Design

-
Learning the Central Events and Participants in Unlabeled Text

-
Exemplar-SVMs for Visual Object Detection, Label Transfer and Image Retrieval
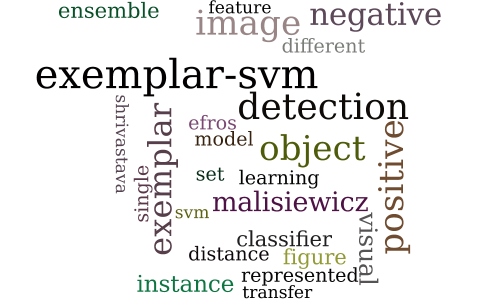
-
Learning Force Control Policies for Compliant Robotic Manipulation

Session 7B — Reinforcement learning 4
chair Michael Bowling, room AT LT 5
-
Agnostic System Identification for Model-Based Reinforcement Learning

-
Greedy Algorithms for Sparse Reinforcement Learning

-
On the Sample Complexity of Reinforcement Learning with a Generative Model

-
Artist Agent: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Automatic Stroke Generation in Oriental Ink Painting

-
Path Integral Policy Improvement with Covariance Matrix Adaptation

Session 7C — Clustering 2
chair Raquel Urtasun, room AT LT 1
-
On causal and anticausal learning

-
Revisiting k-means: New Algorithms via Bayesian Nonparametrics

-
Approximate Principal Direction Trees
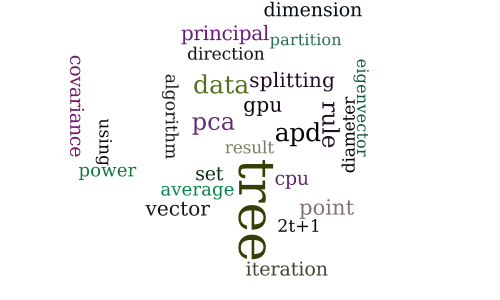
-
Clustering using Max-norm Constrained Optimization

-
Efficient Active Algorithms for Hierarchical Clustering

-
Convergence of the EM Algorithm for Gaussian Mixtures with Unbalanced Mixing Coefficients

-
Groupwise Constrained Reconstruction for Subspace Clustering

-
Clustering by Low-Rank Doubly Stochastic Matrix Decomposition

Session 7D — Supervised learning 2
chair Leon Bottou, room AT LT 2
-
Total Variation and Euler's Elastica for Supervised Learning

-
Flexible Modeling of Latent Task Structures in Multitask Learning

-
Fast classification using sparse decision DAGs
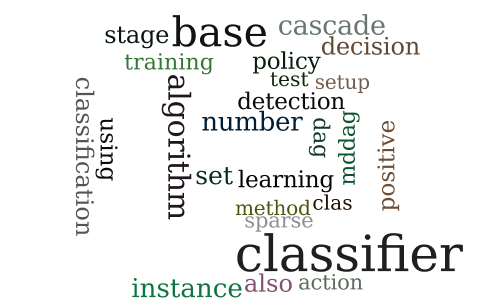
-
An Efficient Approach to Sparse Linear Discriminant Analysis

-
Sequential Nonparametric Regression
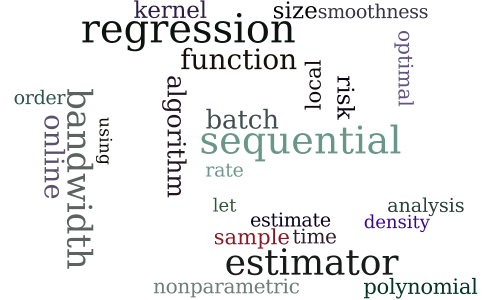
-
The Landmark Selection Method for Multiple Output Prediction
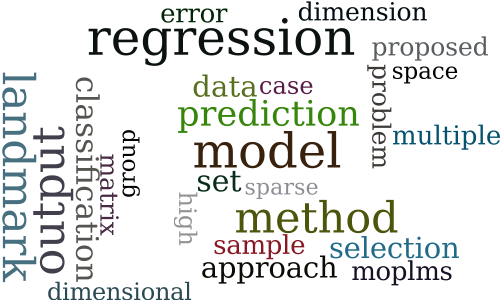
-
Ensemble Methods for Convex Regression with Applications to Geometric Programming Based Circuit Design

-
AOSO-LogitBoost: Adaptive One-Vs-One LogitBoost for Multi-Class Problem

Session 7E — Probabilistic Models
chair Erik Sudderth, room AT LT 3
-
Local Loss Optimization in Operator Models: A New Insight into Spectral Learning

-
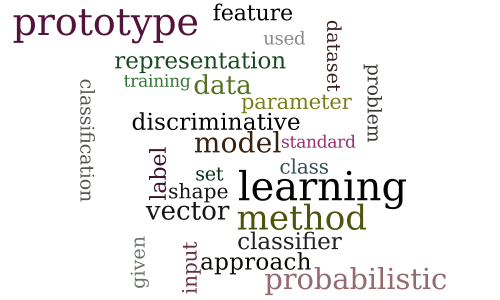
Discriminative Probabilistic Prototype Learning
-
Isoelastic Agents and Wealth Updates in Machine Learning Markets

-
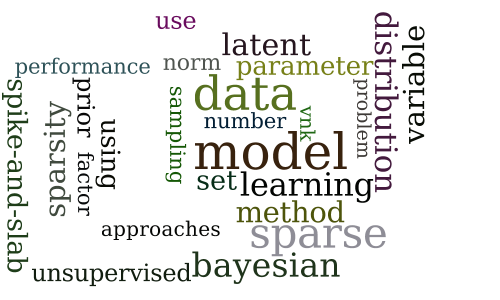
Evaluating Bayesian and L1 Approaches for Sparse Unsupervised Learning
-
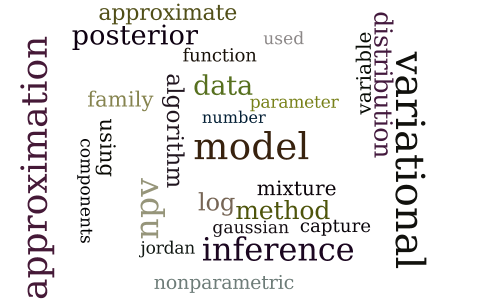
Nonparametric variational inference
-
Levy Measure Decompositions for the Beta and Gamma Processes

-
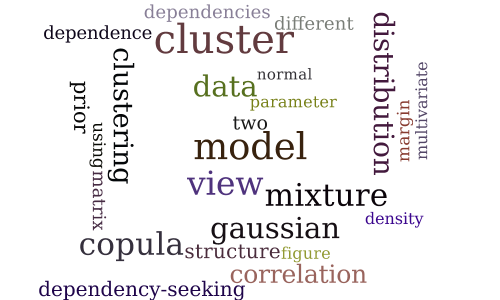
Copula Mixture Model for Dependency-seeking Clustering
-
Predicting accurate probabilities with a ranking loss

Session 8A — Kernel methods 2
chair Mario Marchand, room AT LT 4
-
Copula-based Kernel Dependency Measures

-
The Kernelized Stochastic Batch Perceptron

-
Fast Bounded Online Gradient Descent Algorithms for Scalable Kernel-Based Online Learning

-
Distributed Tree Kernels
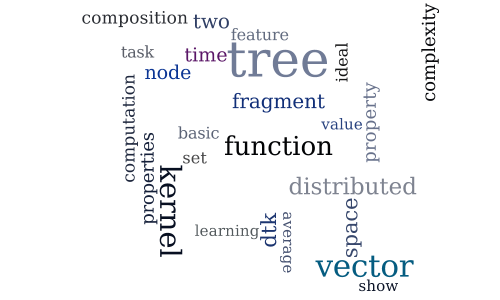
-
Analysis of Kernel Mean Matching under Covariate Shift

Session 8B — Active and cost-sensitive learning
chair Andreas Krause, room AT LT 5
-
The Greedy Miser: Learning under Test-time Budgets

-
Joint Optimization and Variable Selection of High-dimensional Gaussian Processes
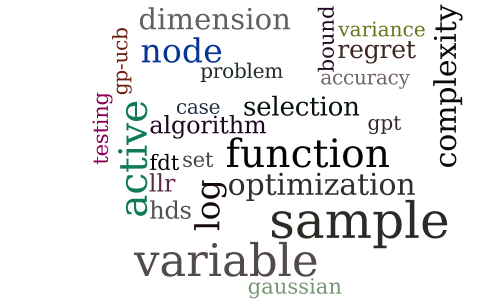
-
Comparison-Based Learning with Rank Nets

-
Bayesian Optimal Active Search and Surveying

-
Hybrid Batch Bayesian Optimization
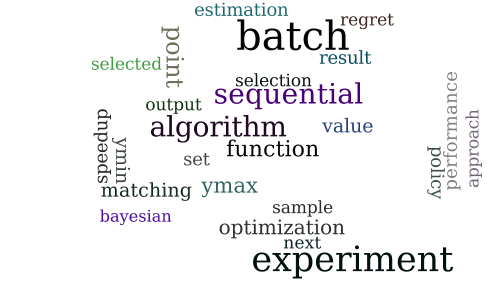
-
Batch Active Learning via Coordinated Matching

-
Bayesian Nonexhaustive Learning for Online Discovery and Modeling of Emerging Classes

Session 8C — Feature selection and dimensionality reduction
chair Andrea Danyluk, room AT LT 1
-
Robust PCA in High-dimension: A Deterministic Approach
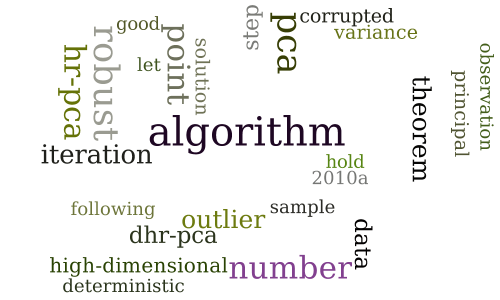
-
Communications Inspired Linear Discriminant Analysis
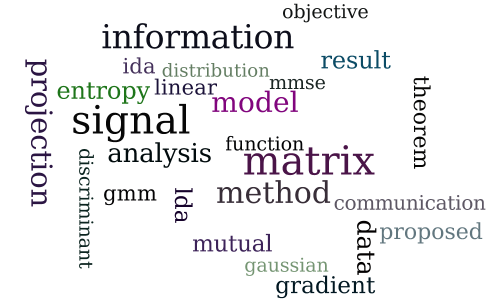
-
Regularizers versus Losses for Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction: A Factored View with New Convex Relaxations

-
Fast Training of Nonlinear Embedding Algorithms

-
Sparse Support Vector Infinite Push

-
Adaptive Canonical Correlation Analysis Based On Matrix Manifolds
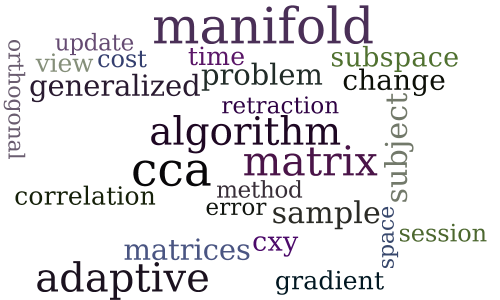
-
Fast approximation of matrix coherence and statistical leverage

-
Feature Selection via Probabilistic Outputs

Session 8D — Recommendation and Matrix Factorization
chair Thorsten Joachims, room AT LT 2
-
A Combinatorial Algebraic Approach for the Identifiability of Low-Rank Matrix Completion

-
Gap Filling in the Plant Kingdom—Trait Prediction Using Hierarchical Probabilistic Matrix Factorization
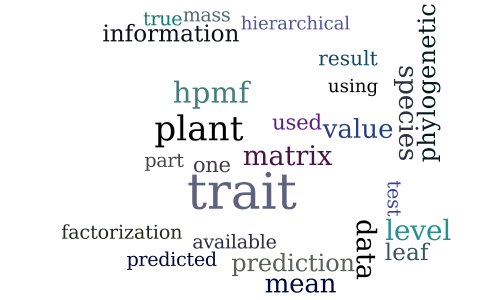
-
Stability of matrix factorization for collaborative filtering

-
Latent Collaborative Retrieval

-
A Bayesian Approach to Approximate Joint Diagonalization of Square Matrices
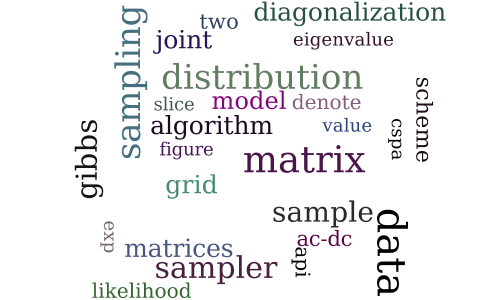
-
Collaborative Topic Regression with Social Matrix Factorization for Recommendation Systems
-
Active Learning for Matching Problems
-
A Graphical Model Formulation of Collaborative Filtering Neighbourhood Methods with Fast Maximum Entropy Training
Session 8E — Graphical models
chair Ricardo Silva, room AT LT 3
-
Variational Bayesian Inference with Stochastic Search
-
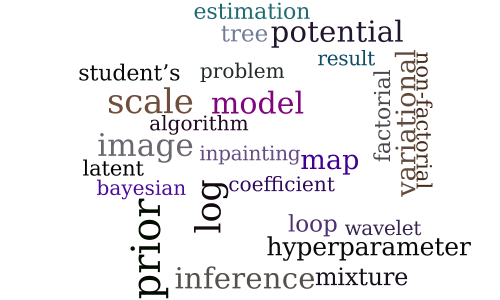
Large Scale Variational Bayesian Inference for Structured Scale Mixture Models
-
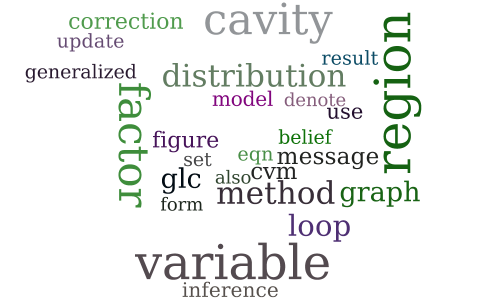
A Generalized Loop Correction Method for Approximate Inference in Graphical Models
-
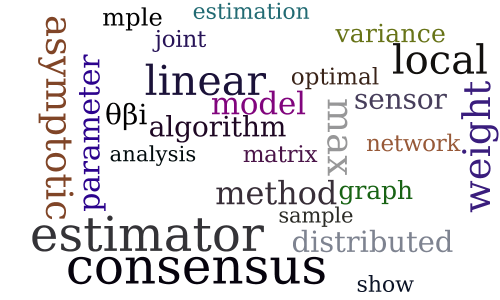
Distributed Parameter Estimation via Pseudo-likelihood
-
High-Dimensional Covariance Decomposition into Sparse Markov and Independence Domains
